Introduction
Sample preparation is one of the most critical and time-consuming steps in analytical workflows across industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food safety, environmental testing, and clinical diagnostics. Errors or inconsistencies at this stage can compromise the accuracy of results, regardless of how advanced the downstream analytical instruments may be. To address these challenges, sample preparation automation instruments have emerged as a transformative solution, delivering higher precision, efficiency, and reproducibility.
Definition
Sample Preparation Automation Instruments are laboratory systems designed to automatically perform routine sample handling steps – such as weighing, dispensing, mixing, dilution, extraction, and purification – prior to analytical testing. These instruments reduce manual labor, improve consistency and reproducibility, minimize human error and contamination, and increase throughput, making them essential in fields like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, environmental testing, and clinical research.
Understanding Sample Preparation Automation
Sample preparation automation refers to the use of automated instruments and robotic systems to perform tasks such as weighing, dilution, extraction, purification, filtration, derivatization, and dispensing. Traditionally, these steps were performed manually, requiring skilled technicians, significant labor hours, and strict adherence to protocols. Automation replaces or augments manual handling with programmable systems that execute protocols consistently and with minimal human intervention.
These instruments are designed to integrate seamlessly with analytical platforms such as chromatography systems (HPLC, GC), mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, and molecular biology analyzers. By standardizing preparation steps, automation reduces variability and improves overall data quality.
Key Types of Sample Preparation Automation Instruments
Sample preparation automation instruments come in various configurations, each tailored to specific applications and sample types.
Liquid Handling Systems
Automated liquid handlers are among the most widely used instruments. They perform tasks such as pipetting, mixing, dilution, reagent addition, and aliquoting. Advanced systems offer high precision at microliter or nanoliter volumes and support high-throughput workflows using multi-well plates.
Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) Automation
Automated SPE systems streamline the purification and concentration of analytes from complex matrices. These instruments are commonly used in pharmaceutical analysis, environmental testing, and food safety. Automation improves recovery rates and reduces solvent usage while ensuring consistent results.
Automated Weighing and Dosing Systems
These instruments automate the weighing of solids and powders, minimizing human error and exposure to hazardous substances. They are particularly valuable in pharmaceutical formulation and chemical research environments.
Robotic Workstations
Robotic sample preparation platforms combine multiple functions – liquid handling, incubation, shaking, heating, cooling, and transfer – into a single automated workflow. These systems are ideal for laboratories requiring flexible, end-to-end automation.
Nucleic Acid and Protein Sample Preparation Systems
In molecular biology and clinical diagnostics, automated instruments are used for DNA, RNA, and protein extraction and purification. These systems improve throughput and reproducibility, especially in high-volume testing laboratories.
Benefits of Sample Preparation Automation Instruments
Improved Accuracy and Reproducibility
Automation eliminates variability caused by manual handling, such as inconsistent pipetting or timing differences. This results in more reliable and reproducible data, which is essential for regulated industries.
Increased Throughput
Automated instruments can process hundreds or thousands of samples per day with minimal supervision. This capability is particularly important in high-throughput screening, clinical testing, and quality control laboratories.
Reduced Labor Costs and Operator Fatigue
By automating repetitive tasks, laboratories can reduce labor requirements and allow skilled personnel to focus on data analysis, method development, and decision-making.
Enhanced Safety
Automation minimizes direct human contact with hazardous chemicals, biohazardous samples, and solvents. This improves laboratory safety and reduces the risk of exposure or contamination.
Standardization and Compliance
Automated systems ensure strict adherence to standardized protocols, which supports compliance with regulatory requirements such as Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP).
Applications Across Industries
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology
Sample preparation automation is widely used in drug discovery, development, and quality control. Automated systems support tasks such as compound screening, bioanalysis, and stability testing, accelerating timelines while maintaining data integrity.
Clinical Diagnostics
In clinical laboratories, automated sample preparation is critical for handling large volumes of patient samples. Instruments used for blood, urine, and tissue sample processing improve turnaround times and reduce the risk of human error.
Food and Beverage Testing
Automation plays a key role in detecting contaminants, residues, and adulterants in food products. Automated extraction and cleanup systems ensure consistent sample processing and reliable results.
Environmental Analysis
Environmental laboratories rely on automated sample preparation for water, soil, and air testing. These instruments improve efficiency and accuracy when analyzing pollutants and trace-level contaminants.
Academic and Research Laboratories
Automation enables researchers to scale experiments, improve reproducibility, and explore complex workflows that would be impractical with manual methods alone.
Key Considerations When Selecting Automation Instruments
When choosing sample preparation automation instruments, laboratories should evaluate several factors:
- Sample type and volume: Compatibility with liquids, solids, or biological samples
- Throughput requirements: Number of samples processed per run or per day
- Flexibility and scalability: Ability to adapt to new methods or increased workloads
- Integration capabilities: Compatibility with existing analytical instruments and laboratory information systems
- Regulatory compliance: Support for validation, audit trails, and documentation
- Cost and return on investment: Initial investment versus long-term operational savings
Careful assessment ensures that the selected system aligns with both current needs and future growth.
Future Trends of Sample Preparation Automation Instruments Market
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Smart Software:
AI-driven software is increasingly being integrated into sample preparation automation instruments to optimize workflows, reduce errors, and enable predictive maintenance. Smart systems can adapt protocols in real time, improving efficiency and data quality.
Growing Demand for High-Throughput Automation:
As laboratories handle larger sample volumes, the demand for high-throughput automated systems continues to rise. Multi-sample processing and faster turnaround times are becoming key purchasing factors across pharmaceutical, clinical, and food testing sectors.
Expansion of Modular and Flexible Platforms:
Manufacturers are focusing on modular designs that allow laboratories to customize and scale automation solutions. Flexible platforms support multiple applications and can be easily upgraded as analytical needs evolve.
Advancements in Miniaturization and Lab-on-a-Chip Technologies:
Miniaturized systems and microfluidic technologies are gaining traction due to their reduced reagent consumption, faster processing, and lower operational costs, supporting sustainable laboratory practices.
Increased Adoption in Emerging Markets:
Rapid growth in healthcare infrastructure, pharmaceutical research, and environmental testing in emerging economies is driving market expansion. Automation adoption is accelerating as laboratories modernize and standardize operations.
Growth Rate of Sample Preparation Automation Instruments Market
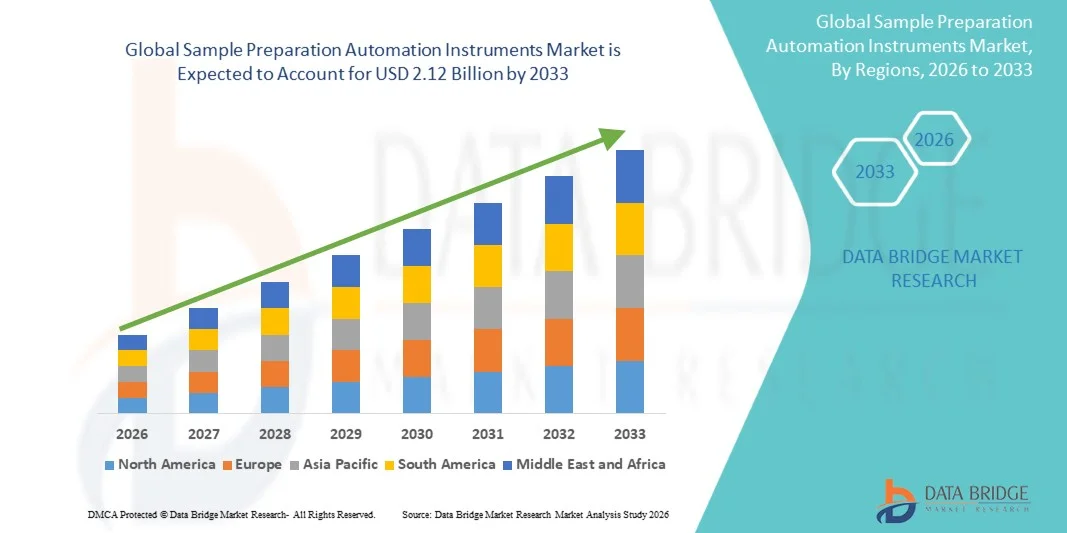
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the sample preparation automation instruments market was estimated to be worth USD 1.02 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.60% to reach USD 2.12 billion by 2033.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-sample-preparation-automation-instruments-market
Conclusion
Sample preparation automation instruments are reshaping modern laboratories by improving accuracy, efficiency, and safety. As analytical demands continue to grow, automation is no longer a luxury but a necessity for organizations seeking reliable results and competitive advantages. By investing in the right automation solutions, laboratories can enhance productivity, ensure data integrity, and meet the evolving challenges of scientific and industrial analysis.