Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, few innovations have created as much excitement and concern – as Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI). From writing poetry to composing complex code, generative models like GPT-series, diffusion models, and transformer-based systems are reshaping entire industries. But beyond creative applications, one of the most critical arenas where generative AI is making a profound impact is cybersecurity.
Definition
Generative AI Cybersecurity refers to the application of generative artificial intelligence models to enhance cyber defense and resilience by proactively detecting, predicting, and responding to security threats. It involves using AI systems that can generate insights, simulations, code, or automated responses to identify vulnerabilities, analyze attack patterns, create defensive strategies, and support security operations, while also addressing risks introduced by the misuse or compromise of generative AI itself.
What Is Generative AI? A Quick Primer
Generative AI refers to models capable of creating new content – text, images, code, or even synthetic data – based on patterns learned from large datasets. Unlike traditional AI, which is often trained to classify or predict, generative models can “invent” new outputs that resemble real examples. This creative ability enables both powerful defensive tools and, unfortunately, sophisticated offensive techniques.
Opportunities: How Generative AI Strengthens Cybersecurity
1. Enhanced Threat Detection
One of the biggest challenges in cybersecurity is identifying threats buried within mountains of data. Traditional rule-based systems struggle to adapt to novel attacks. Generative AI, by contrast, can learn normal network behavior and detect subtle deviations that signal compromise.
For instance, generative models can simulate normal traffic patterns and use anomaly detection to flag unusual activity, often before signature-based systems notice anything suspicious.
2. Automated Incident Response
Responding to a breach quickly is just as important as detecting it. Generative AI can automate response playbooks, draft remediation steps, and even initiate containment actions based on real-time analysis. This reduces response time and helps organizations operate more like a 24×7 security operations center (SOC) without bottlenecks.
3. Security Tool Automation
Security professionals spend significant time configuring tools, writing scripts, and analyzing logs. Generative AI can automate many of these repetitive tasks – creating scripts, generating firewall rules, or summarizing threat reports – freeing analysts to focus on high-value strategic work.
For example, an AI model might generate a script to parse server logs faster or automate patch workflows across an enterprise environment.
4. Simulated Attack Scenarios
Generative AI can produce realistically simulated attacks (often referred to as red-teaming) to test defenses. By generating plausible exploits, defenders can preemptively strengthen weak points in their infrastructure.
Such simulations help organizations build resilience through continuous testing and refinement, rather than waiting for real attacks.
5. Training and Skill Development
Cybersecurity talent shortages are a persistent challenge. Generative AI can act as an on-demand tutor, generating realistic scenarios for training purposes, explaining complex concepts, or guiding junior analysts through incident response.
It can even create adaptive learning modules tailored to individual skill levels, accelerating workforce development.
Risks of Generative AI in Cybersecurity
Despite its benefits, generative AI also introduces new dangers – especially when misused by malicious actors.
1. Automated Phishing and Social Engineering
Generative AI can craft highly convincing phishing emails or social engineering campaigns that mimic writing styles, corporate communications, and contextual cues. This greatly increases the likelihood of tricking targets, making once-obvious phishing attempts increasingly difficult to spot.
Attackers can leverage AI to produce personalized messages at scale, exponentially increasing the volume and quality of social engineering attacks.
2. Creation of Malicious Code
Rather than relying on skilled programmers, attackers can use generative AI to write exploit code or malware automatically. Given a description of a vulnerability, AI models can potentially generate proof-of-concept exploit code that works in real environments.
This lowers the entry barrier to cybercrime and speeds up the attack lifecycle.
3. Synthetic Identity and Deepfakes
Generative AI powers deepfakes and synthetic identities – convincing yet fake digital personas that can elude verification systems. Cybercriminals can use these assets to infiltrate organizations, commit fraud, or bypass identity checks.
As deepfake technology becomes more accessible, traditional authentication methods may no longer be sufficient.
4. Adversarial Attacks on AI
Ironically, as defenders adopt AI, attackers will target these very systems. Generative models are susceptible to poisoning and adversarial manipulation, where carefully crafted input can mislead the model into making incorrect predictions or classifications.
This opens a novel threat vector: AI vs. AI warfare, where attackers manipulate AI defenses against themselves.
5. Over-Reliance and Skill Degradation
Heavy dependence on AI tools can erode fundamental cybersecurity skills. If analysts defer judgment too quickly to AI suggestions, they may miss nuanced threats or fail to understand the logic behind decisions – reducing human oversight in critical processes.
The Future of Digital Defense: Co-existence and Collaboration
Generative AI will not replace cybersecurity professionals – but it will redefine their roles. The future likely involves a human-in-the-loop model, where AI augments human capabilities without supplanting them.
Here’s what the next decade could bring:
1. AI-Powered Security Platforms
We can expect platforms that blend generative AI with traditional cybersecurity functions: automated detection, predictive risk analysis, and self-healing systems that instinctively respond to threats based on learned patterns.
2. Democratized Cyber Defense
Small and medium organizations – previously unable to afford robust security teams—can leverage AI to level the playing field. AI-driven tools make advanced defenses accessible, reducing gaps between large enterprises and smaller firms.
3. Regulation and Ethical Standards
As AI becomes central to cybersecurity, regulatory frameworks will emerge to govern its use. Policies on ethical AI deployment, transparency, and accountability will be crucial to balance innovation with safety.
4. AI-to-AI Defense Ecosystems
The arms race between attackers and defenders will increasingly involve AI on both sides. Real-time adaptive defenses and self-learning systems will counter AI-generated threats by analyzing patterns faster than humans can react.
5. Enhanced Collaborative Intelligence
Generative AI may facilitate collaboration across organizations, where anonymized threat intelligence is shared and used to improve collective defense. This networked approach can help anticipate emerging attacks globally.
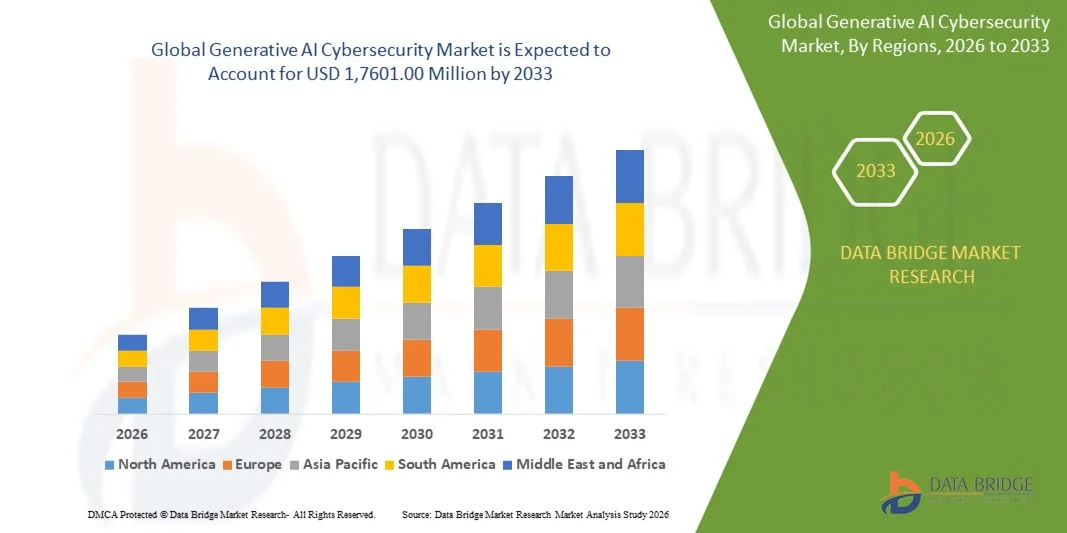
Growth Rate of Generative AI Cybersecurity Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global generative AI cybersecurity market was estimated at USD 976.14 million in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 43.55% to reach USD 1,7601.00 million by 2033.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-generative-ai-cybersecurity-market
Conclusion
Generative AI is reshaping the cybersecurity landscape by offering powerful tools to detect threats, automate defenses, and strengthen digital resilience, while simultaneously introducing new risks when exploited by malicious actors. Its impact underscores the need for a balanced approach – one that combines advanced AI capabilities with strong governance, ethical oversight, and human expertise. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations that strategically integrate generative AI into their security frameworks will be better equipped to safeguard their digital ecosystems and stay ahead in the ongoing battle for cyber defense.